AI Agents in Military Use: integrating LLMs and Autonomous Systems on the Frontline

When Vladimir Putin declared in 2017 that "whoever leads in AI will dominate the world," he predicted future wars would be fought by autonomous drones rather than human soldiers. That prediction has become reality with a chilling speed. In Ukraine today, drones now cause 70-80% of battlefield casualties, changing how wars are fought. What was once science fiction, machines making life-and-death decisions, has become an urgent reality that militaries, ethicists, and policymakers worldwide must grapple with.
The transformation is breathtaking in scope: AI agents now assist in everything from identifying targets in milliseconds to coordinating complex logistics across continents. But as these digital warriors gain autonomy and lethality, they raise profound questions about accountability, ethics, and the future of human agency in warfare.
From DART to Drones: The Evolution of Military AI
The military's relationship with artificial intelligence began modestly but proved its worth quickly. During the 1991 Gulf War, the U.S. military deployed DART, a DARPA-funded logistics system that used intelligent software agents to optimize transport and supply movements. This early AI success story reportedly saved millions of dollars shortly after launch, demonstrating that machines could enhance military efficiency in ways previously unimaginable.
The strategic importance of AI crystallized in 2014 when the U.S. Department of Defense announced its "Third Offset Strategy" explicitly identifying AI and autonomy as keys to maintaining military superiority. This declaration triggered a global arms race that continues to accelerate. China unveiled its Next Generation AI Development Plan with the audacious goal of achieving world domination in AI by 2030. Russia's proclamation about AI supremacy leading to global dominance underscored that this was about survival and supremacy.
A watershed moment came in 2017 with Project Maven, officially known as the Algorithmic Warfare Cross-Functional Team. This initiative applied machine learning to the overwhelming volume of drone surveillance footage, using computer vision to automatically detect and classify potential targets. The project sparked controversy when Google employees protested their company's involvement, leading to Google's withdrawal in 2018. Yet by 2024, the Pentagon credited Project Maven with providing crucial targeting support for U.S. military operations in the Middle East.
The evolution reached a new pinnacle in 2023 when DARPA's Air Combat Evolution program achieved the first-ever live dogfight between an AI-controlled F-16 and a human pilot. The AI successfully executed autonomous tactical maneuvers within visual range, a feat unimaginable just a decade earlier. This milestone demonstrated that AI had evolved from a back-office tool to a front-line combatant.
How AI Agents Are Being Deployed Today
Modern militaries deploy AI across an astonishing range of applications, fundamentally reshaping warfare at every level.
Intelligence and Targeting
- Project Maven's algorithms flag potential targets in drone footage, while Israel has developed more advanced systems like "Gospel" and "Lavender."
- The Gospel system analyzes surveillance data from multiple sources: drones, intercepted communications, satellite imagery, to generate target recommendations at unprecedented speed, reportedly producing 100 new targets per day during operations.
- Lavender uses AI to comb through databases and flag individuals likely affiliated with enemy forces, creating what amounts to an algorithmic kill list.
Autonomous Defense Systems
- The U.S. Navy's Phalanx CIWS and Israel's Iron Dome use automated target recognition to shoot down incoming threats within seconds, far faster than any human could react.
- India's new Indrajaal drone defense dome represents the next evolution: an AI-powered system capable of monitoring 4,000 square kilometers of airspace, autonomously detecting and neutralizing everything from single drones to coordinated swarm attacks.
Logistics and Maintenance
- Predictive algorithms analyze sensor data from military equipment to forecast failures before they occur.
- The U.S. Air Force found that machine learning models could outperform traditional methods in predicting aircraft part failures, though implementing these systems at scale requires extensive data engineering.
- Autonomous supply convoys and robotic vehicles are being tested to deliver materiel without risking human drivers.
Combat Enhancement
- Ukraine's integration of AI into FPV (First-Person View) attack drones has revolutionized battlefield effectiveness, boosting drone strike accuracy from 30-50% to roughly 80%.
- These AI-enhanced drones can recognize targets, stabilize attack trajectories, and maintain effectiveness even when communications are jammed.
The Human Cost: Ethical Dilemmas and Dangers
The acceleration of AI warfare brings profound ethical challenges that military leaders and societies must confront.
The accountability gap looms largest: when an AI system makes a lethal mistake, who bears responsibility? The commander who deployed it? The programmer who coded it? The data scientist who trained it? Israeli officers have acknowledged spending "mere seconds” vetting each AI-generated target during intense operations. When machines recommend targets faster than humans can thoughtfully evaluate them, the risk of tragic errors multiplies.
Algorithmic bias presents another insidious danger. AI systems learn from data, and if that data contains human prejudices, the AI perpetuates and amplifies them. The International Committee of the Red Cross warns that an AI trained on biased data might consistently misidentify civilians as combatants based on superficial features like ethnic attire or demographics. Unlike a human soldier who can recognize cultural nuances, a machine may apply blunt, discriminatory criteria.
The black box problem compounds these issues. Most advanced AI operates in ways humans cannot fully understand or explain. When a drone's AI recommends striking a building, commanders need confidence in the rationale. But neural networks' inherent complexity means that even their creators often cannot explain why they made a particular decision. This opacity undermines trust and makes it nearly impossible to audit AI decisions against the laws of war.
One of the biggest unsolved challenges, both in military and civilian AI, is transparent decision-making. PromptLayer addresses this by giving teams full traceability, logging, and evaluation tools for every AI agent decision. Ensuring oversight is essential for anyone deploying autonomous systems.
Most troubling is the speed versus judgment dilemma. AI operates at machine speed, potentially escalating conflicts faster than humans can intervene. The pressure to match an adversary's AI-driven tempo could lead to a "flash war" scenario where algorithms drive escalation beyond human control. As conflicts accelerate, the time for moral reflection and strategic consideration evaporates.
The Global Response: Policies and Red Lines
The international community is grappling with the rise of AI in warfare, leading to a mix of new declarations, strong moral stances, and intense debate.
- A New Political Framework:
- The United States introduced the "Political Declaration on Responsible Military Use of AI and Autonomy" in February 2023.
- As of 2024, 51 countries have endorsed this non-binding framework.
- Its goal is to build political commitment around human accountability and risk mitigation, aiming to prevent AI from undermining global stability.
- The Moral & Religious Line:
- Moral authorities are adding their voices to the conversation.
- The Vatican's 2024 document on AI ethics issued a clear decree: "No machine should ever choose to take the life of a human being."
- This highlights a widespread call for AI to complement, not replace, human moral judgment in life-and-death decisions.
- Industry's Dual Response:
- Defense and tech companies are actively innovating while also focusing on safety.
- Lockheed Martin launched Astris AI in 2024, a subsidiary dedicated to "trustworthy AI" for defense.
- Partnerships like the Anduril-OpenAI collaboration show that traditional tech companies are increasingly entering the national security space.
- The "Killer Robot" Debate:
- The debate over lethal autonomous weapons (LAWs) is intensifying at the United Nations.
- Two Sides: 22 countries are pushing for an outright ban on "killer robots."
- The Middle Ground: Others argue for systems that maintain "meaningful human control," ensuring a human-in-the-loop for final targeting decisions.
- The Core Challenge: A clear, future-proof definition of "meaningful human control" remains elusive as AI technology accelerates.
Ukraine's Laboratory: AI Warfare in Real Time
The Ukraine conflict has become an unprecedented testing ground for AI warfare, providing real-world data on both capabilities and limitations.
Drone swarms coordinating attacks autonomously have moved from concept to battlefield reality. Ukrainian forces report experimenting with AI systems that allow multiple drones to share information and coordinate strikes without constant human direction. These swarms can overwhelm traditional defenses through sheer numbers and adaptive tactics.
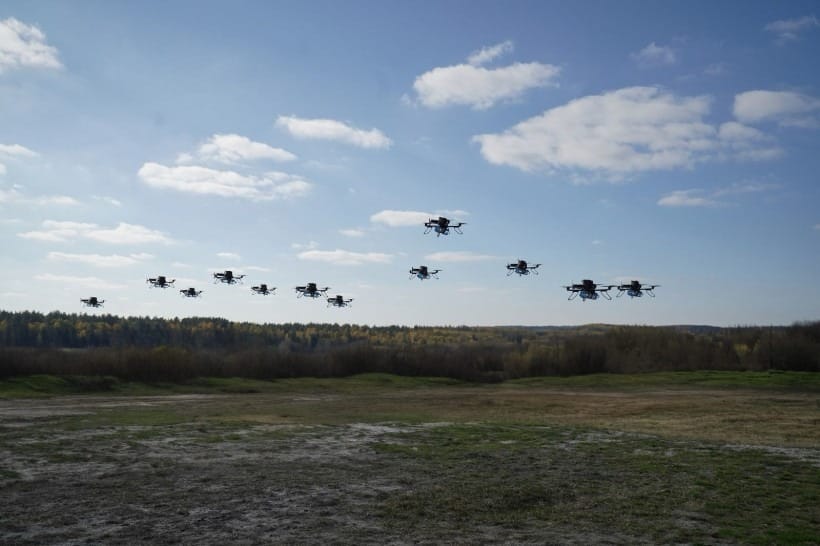

The 80% accuracy rate achieved by AI-enhanced drones has transformed battlefield dynamics. Where previously a drone operator might need multiple attempts to hit a target, AI guidance means that even relatively inexperienced operators can achieve devastating precision. This democratization of lethality has profound implications for future conflicts.
The conflict has created a data goldmine for AI development. Every engagement provides information to refine algorithms and improve performance. This rapid iteration cycle means that AI systems deployed at the conflict's start bear little resemblance to current versions. The battlefield has become a laboratory where AI evolution is measured in weeks.
Harnessing AI Without Losing Humanity
AI agents offer military forces unprecedented advantages, from the logistics systems that saved millions during the Gulf War to the targeting algorithms that can process vast intelligence streams in seconds. The technology has evolved from experimental curiosity to battlefield necessity with stunning speed. In Ukraine, AI-enhanced drones achieve accuracy rates that transform cheap commercial hardware into precision weapons. Defense systems like Iron Dome save lives by reacting faster than any human could.
Yet these capabilities come with profound risks that demand our urgent attention. When algorithms can recommend targets faster than humans can evaluate them, when bias encoded in data can lead to discriminatory killing, when the fog of war meets the black box of AI, we enter dangerous territory that challenges our concepts of accountability, ethics, and human agency in warfare.
The transformation is already underway. The question is whether humanity can harness this technology's benefits while preserving the moral and strategic judgment that only humans can provide. In this new era of algorithmic warfare, our survival may depend on maintaining human control over the machines we create.